UV test also known as UV aging test which is a process of simulating the various factors involved in the actual use of the product to carry out corresponding conditions to strengthen the experiment on the aging of the product. The UV aging test experiment is mainly for plastic materials, and the common aging mainly includes light aging, damp heat aging, hot air aging. The ultraviolet aging test chamber uses fluorescent ultraviolet lamps as the light source, and performs accelerated weather resistance tests on materials by simulating the ultraviolet radiation and condensation in natural sunlight to obtain the results of the weather resistance of the materials. It can simulate environmental conditions such as ultraviolet, rain, high temperature, high humidity, condensation, darkness, etc. in the natural climate. By reproducing these conditions, they can be combined into a cycle and let it automatically execute the cycle times.

fluorescent ultraviolet lamps
Some outdoor products are exposed to the sun for a long time, so the yellowing resistance test and aging resistance test of the product are very important. To understand the service life of the product outdoors, it is necessary to carry out an ultraviolet aging test simulation test, which is also a UV test. Since the intensity of the UV test performed in the laboratory is greater than the intensity of outdoor light, the UV aging test can save some test time for staff and the outdoor service life of the product can be obtained in a short time. UV ultraviolet light aging test chamber, ultraviolet weathering test chamber quickly and truly reproduce the damage of sunlight, rain, and dew to materials: only a few days or weeks, the UV aging test chamber can reproduce the outdoor need several months or damage that takes years to produce: including fading, discoloration, decreased brightness, chalking, cracking, blurring, embrittlement, strength reduction, and oxidation. The ultraviolet aging test chamber is suitable for the aging test of non-metallic materials’ resistance to sunlight and artificial light sources. The light source uses 8 ultraviolet fluorescent lamps with a rated power of 40W as the light source. Ultraviolet fluorescent tubes are distributed on both sides of the machine, 4 on each side. (There are UVA-340 and UVB-313 light sources for users to choose and configure).
UV aging test range
Non-metallic materials, organic materials (for example: coatings, paints, dyes, fabrics, printing and packaging, adhesives, automotive and motorcycle industry parts, cosmetics, metals, electronics, electroplating, rubber, plastics and their products, etc.) LISUN designed and manufacture UV Aging Test Chamber fully complies with the requirements of Standard ISO 4892-1, ISO 4892-3, GB/T16585-1996, GB14522-93, GB/T16422.3-1997, ASTMG53 and etc.
There are two ways of exposure:
The first type:
1. After the sample has been exposed to light for a period of time, it is followed by a non-irradiation period (that is, the temperature changes and condensation is formed on the sample) cyclic test. The test period is in accordance with relevant standards. If there is no specified cycle condition, the following cycle is recommended:
2. Irradiation exposure for 4h or 8h at a black standard temperature of 60℃±3℃, and then 4h exposure without radiation condensation at a black standard temperature of 50℃±3℃.
Note: The aging degradation of some polymers (such as PVC) is very sensitive to temperature. In this case, it is recommended to use a radiation exposure temperature below 60°C (such as 50°C) to simulate a colder climate.
3. When the radiation exposure and condensation exposure procedure is selected, the shortest allowable radiation or condensation exposure period is 2h to ensure that the conditions of each exposure period reach a balance.
The second type:
1. The sample is continuously exposed to radiation and has a cyclic test of regular water spray. Relevant standards and regulations during the trial period. If not specified, the following test conditions are recommended.
2. Radiation exposure for 5h under the black standard temperature of 50℃±3℃ and air relative humidity (10±5)﹪, and then continue the radiation exposure and spray water for 1h at the black standard temperature of 20℃±3℃.
Notice:
I. Use a moisture condenser in the equipment to make the exposed surface of the sample wet. Moisture is generated by heating water in a container placed under the sample rack.
II. When the equipment does not meet the exposure method 1, a method of controlling the relative humidity in the exposure room can be adopted, or a method of spraying the sample with pure water or an aqueous solution that simulates acid rain can be adopted. Refer to the requirements of GB/T9344-88 for water use.
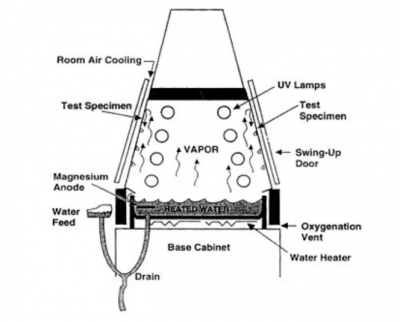
UV Test Process
The choice of UV fluorescent lamp:
The advantages of fluorescent lamps are: fast test results are obtained; simplified illuminance control; stable spectrum; only little maintenance is required; the price is cheap, and the operating cost is reasonable.
There is only a small part of the land on the earth, and most of the area is the ocean. Therefore, the ocean climate is a climate environment that has a great impact on human life and material products.
It only takes a few days or a few weeks, and the UV aging test can reproduce the damage that takes months or years outdoors. The damage caused mainly includes fading, discoloration, decrease in brightness, chalking, cracking, blurring, embrittlement, decrease in strength and oxidation.
UV lamp selection UVA340, UVB313, UVC lamp introduction
UV fluorescent ultraviolet lamps can simulate the most important short-wave ultraviolet light in sunlight and reproduce the aging of the physical properties of materials caused by light. According to different test conditions, there are several different ultraviolet lamps to choose.
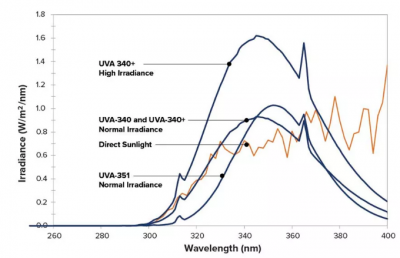
UVA tube
The UVA-340 tube can well simulate the sunlight in the critical short-wave region from 365nm to 295nm.
UVA-340+ lamps can be tested under the conditions of reaching or exceeding the maximum irradiance of 1.70 W/m2/nm, which meets the highest irradiance value required in the main test standards.
The UVA-351 tube simulates the ultraviolet part of the sunlight passing through the window glass. Cool white lamps can also be used to simulate an office environment.
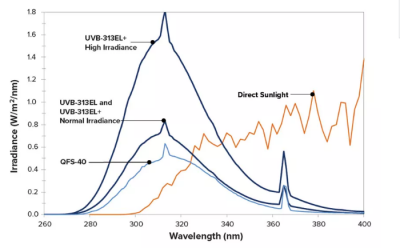
UVB tube
UVB-313EL (formerly QFS-40) tube produces short-wave ultraviolet light that is stronger than the sun’s ultraviolet rays that usually irradiate the surface of the earth. UVB-313 tube is mainly used for quality control and product development, or is a material with strong weather resistance carry out testing.
UVB-311EL+ lamps can also provide the most demanding fluorescent UV tests with high irradiance levels. When using UVB lamps, you should be taken to ensure the authenticity of the failure mechanism.
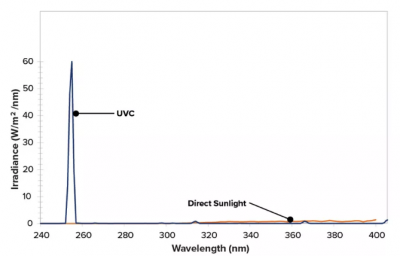
UVC tube
The ultraviolet lamp tube produces ultra-strong short-wave ultraviolet light at 254nm, which is far below the limit of sunlight. This represents the most common UVC ultraviolet radiation used for surface disinfection. Although ultraviolet light can effectively kill these pathogens, it can also cause degradation of plastics, coatings and fabrics. UVC ultraviolet lamps reproduce this destructive irradiance to evaluate the durability of materials exposed to UVC ultraviolet rays.
Except UV/basic, other models of UV ultraviolet aging test chamber are equipped with solar eye irradiance control system, which can monitor and accurately maintain the set irradiance intensity by adjusting the output of the lamp, so as to correct the intensity of the lamp. Differences caused by batch differences, environmental temperature changes, and lamp aging. The difference in irradiance may affect the aging speed and aging mode of the material, so irradiance control is very important. Note: UV/BASIC models adjust the irradiance level through lamp rotation.
Equipment with solar eye irradiance control system can set the irradiance level. For example, for the UVA-340 lamp, the irradiance of 0.89W/m2@340nm is set to be equivalent to the intensity at noon in summer. In order to get the test results faster, the UV aging chamber can be set to run under the condition of 200% light intensity at noon in summer. Based on different lamp types, the table below lists the highest irradiance levels and some commonly used irradiance setting points.
Preparation before test:
1. Power requirements: AC380V±10% 50±0.5Hz three-phase five-wire system
2. The user is required to configure the corresponding capacity air or power switch for the equipment at the installation site
3. Purified water, distilled water, and deionized water are used for the water supply of the instrument. Resistivity≥500Ω.m
4. Prepare experimental samples
5. Ambient temperature: 5℃~+30℃ (average temperature within 24 hours≤30℃)
6. Environmental humidity: ≤85%RH
Test Steps:
1. Connect the power supply and ground wire.
2. Open the door and place the test product.
3. Set “Total Test Time” and “Lighting Time”.
4. A “Total Timing” time controller has three gears, “h”, “M” and “S” stand for hour, minute, and second respectively. Select the travel time by scrolling up and down.
5. B “lighting time”, you can set the mutual conversion of “lighting” and “humidity is condensation”, that is, lighting (lighting during the day) and humidity (condensing at night). Operation refer to “item A”
6. Press the “start” and “light” keys, the test box will start to run automatically
7. Temperature setting.
8. A Press the “mode button” on the surface of the QUV ultraviolet weathering tester, and press “^^ to adjust the temperature. After the adjustment is completed, press the “mode button” to return, the word is stable and does not flash, and the setting is complete.
9. For the humidity value of B, please refer to the “Comparison Table” according to the method listed above.
10. After the above settings are completed, the device enters the running state.
11. At the end of the total test time, all instruments stop working, and the QUV ultraviolet weathering test box is in standby.
12. Open the door and take out the test product.
13. When a separate light test is required, please set the “lighting timing” to the same time as the “total time” and set the other side to the “maximum value”.
Prohibited test items
Explosive:
• Nitroglycol (ethylene glycol dinitrate), nitroglycerin (glycerol trinitrate), nitrocellulose and other explosive nitrate esters.
• Trinitrobenzene, trinitrotoluene, trinitrophenol (picric acid) and other explosive nitro compounds.
• Peracetic acid, methyl ethyl ketone peroxide, benzoyl peroxide and other organic peroxides.
Combustibles:
Spontaneous combustion: metals: “lithium”, “potassium”, “sodium”, yellow phosphorus, phosphorus sulfide, red phosphorus. Celluloid: calcium carbide (calcium carbide), phosphating lime, magnesium powder, aluminum powder, sodium bisulfite.
Oxide properties:
• Potassium chlorate, sodium chlorate, ammonium chlorate and other chlorates.
• Potassium peroxoate, sodium peroxoate, ammonium peroxoate and other peroxy acid salts.
• Potassium peroxide, sodium peroxide, barium peroxide and other inorganic peroxides.
• Potassium nitrate, sodium nitrate and other nitrates.
• Potassium hypochlorite and other hypochlorites.
• Sodium chlorite and other chlorites.
Flammables:
• Ether, gasoline, acetaldehyde, propylene oxide, carbon disulfide and other substances whose ignition point is less than -30℃.
• Ordinary ethane, ethylene oxide, acetone, benzene, methyl ethyl ketone and other substances whose ignition point is above -30℃ but below 0℃.
• Methanol, ethanol, xylene, amyl acetate and other substances whose ignition point is above 0℃ and below 30℃.
• Kerosene, gasoline, turpentine, isoamyl alcohol, acid vinegar and other substances whose ignition point is above 30℃ and below 65℃.
Flammable gas:
Hydrogen, acetylene, ethylene, methane, ethane, propane, butane and other gases that may burn at 1 atmosphere at a temperature of 15°C.
Precautions:
1. Do not look directly at the lighted tube at close range.
2. Although avoid bare skin under the lighted tube.
3. It is strictly forbidden to open the door during the test.
4. Please check the water level when the water shortage light is on.
Lisun Instruments Limited was found by LISUN GROUP in 2003. LISUN quality system has been strictly certified by ISO9001:2015. As a CIE Membership, LISUN products are designed based on CIE, IEC and other international or national standards. All products passed CE certificate and authenticated by the third party lab.
Our main products are Goniophotometer, Integrating Sphere, Spectroradiometer, Surge Generator, ESD Simulator, EMI Receiver, EMC Test Equipment, Electrical Safety Tester, Environmental Chamber, Temperature Chamber, Climate Chamber, Thermal Chamber, Salt Spray Test, Dust Test Chamber, Waterproof Test, RoHS Test (EDXRF), Glow Wire Test and Needle Flame Test.
Please feel free to contact us if you need any support.
Tech Dep: Service@Lisungroup.com, Cell/WhatsApp:+8615317907381
Sales Dep: Sales@Lisungroup.com, Cell/WhatsApp:+8618917996096
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *