A goniophotometer is a measuring device. It is used to measure directional light distribution characteristics in lamps and luminaires. It collects photometric data from different spherical locations.
Then it creates a web of photometric data that encircles the item under test. Gonio photometric data is obtained using a variety of instruments and is delivered in a variety of angular coordinate systems.
The LSG-6000 Moving Detector Goniophotometer (Mirror Type C) fully complies with the standards of LM-79-19, IES LM-80-08, COMMISSION DELEGATED REGULATION (EU) 2019/2015, CIE-121, CIE S025, SASO 2902, IS16106, and EN13032-1 clause 6.1.1.3 type 4. LSG-6000 is the most updated product of the LSG-5000 and LSG-3000 in accordance with the LM-79-19 standard.
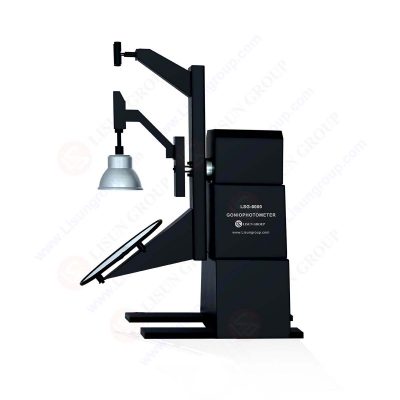

LM-79 Moving Detector Goniophotometer
The amount of light shining in a specific direction is measured by gonio photometry. The word “gonio” comes from the Greek word “gonio,” which means “angle.” Gonio photometry is the measurement of a light source’s angular or spatial distribution of light.
A laser can be a very powerful light source. The beam is usually small and travels in a near-perfect straight line. This makes a laser ineffective in daily life use. An incandescent lamp is a nearly perfect isotropic radiator.
It produces nearly equal intensity in all directions. This is one of the reasons why tungsten lamps are a better source of light for lighting our homes and offices.
In 2001, the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IESNA is commonly abbreviated as “IES”) published a standard called LM-75-01 (since updated in 2019 to LM-75-19). It defined three generic types of goniometer motion. Type A, B, and C are the three types.
The motion of type A and B goniophotometers is very similar. The device under test is rotated 90° about orthogonal horizontal and vertical axes in both cases. The corresponding type A or B coordinate system is referred to as horizontal-vertical (H-V or X-Y). A type C goniophotometer rotates the device under test about an azimuthal axis.
This is the nadir angle which is usually aligned along the polar axis of the coordinate system. While the elevation or inclination axis is the other axis of motion. The type C spherical coordinate system is abbreviated as – with (theta) representing the elevation axis and (psi) representing the azimuthal axis.
Type C goniophotometers are usually used for measuring lamps and architectural lighting products. Some manufacturers have designed type C goniophotometers with an accessory kit. This helps convert it to type B motion (and vice versa).
This adaptability allows a single goniophotometer to accommodate almost any type of light source. These include directional vehicle lighting and architectural luminaires. The moving detector or moving mirror goniophotometers use type C motion. In this, the device under test is held vertically and shining down or shining up.
During a measurement, the lamp’s orientation with respect to gravity remains constant. Over a range of 0-360°, the first axis of rotation revolves around the vertical azimuthal axis, (psi). The elevation or inclination (theta) is the second axis of rotation and is applied to either the mirror or the detector. Which then rotates about the light source over a range of 0-180°.
There are four key factors for measuring the luminous intensity distribution. These are stability of the tested lamps, the measuring distance, angle, and luminance.
It is critical to ensure that the test light source is always operating in a stable state. This allows for precise distance, luminance, and relative rotation angle measurements between the tested luminaries and the photometer.
The near field detector and the large mirror move in a straight line. The far-field detector and the massive mirror both move simultaneously. The burning positions of the luminaires will be maintained without movement. The detector will always detect light directly from the luminaires.
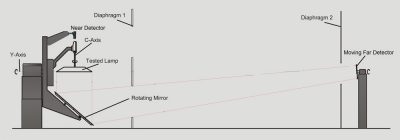
LSG-6000 Moving Detector Goniophotometer Working Principle
The German angle decoding system and Japanese rotary motor enable LISUN’s goniophotometer to rotate smoothly and accurately. It also provides stability when it starts and stops. The working principles are also IESNA and CIE compliant.
A rotational lamp holder, a revolving mirror, and a photometer make up a rotating mirror goniometer. The lamp is guided in a circular path around the revolving mirror. This directs the light toward the photometer head while maintaining a consistent orientation.
The spectral change caused by the mirror is compensated. This is done by adjusting the photometer head to the spectral luminous efficiency curve of the human eye. The photometer is fixed in place but each version is in a different position just as the lamp rotators and various perforations in the measurement space help to reduce scattered light.
Rotating mirror goniometers in a circuit move the light source around the mirror rather than the other way around. Here is only one theta axis. It is at the same level as the center of the light source to be measured. Both this axis and the tilted mirror have been reversed.
This type of construction allows an increase in the distance between the lamp and the mirror. The followed decrease in the overall height of the structure reduces zig-zag reflections between the lamp and the mirror. The opening facing the photometer head is then either conical to collect light from multiple spatial positions or the detector and tube are rotated synchronously with the mirror and with the same radius.
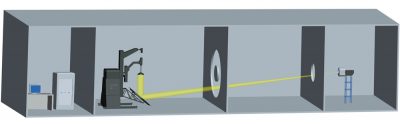
LSG-6000 Moving Detector Goniophotometer Dark Room
The luminaire revolves around the vertical axis during the test. While the reflector revolves around the horizontal axis. The synchronization axis rotates in the opposite direction. The synchronized rotation of the luminaire and reflector can be easily measured.
This can be done at any horizontal or vertical angle without tilting the luminaire. The detector is placed in front of the reflector with a limited metering distance. This is to capture light from all directions. After measuring the luminance value the light intensity value is calculated. This calculation is based on the distance between the light source and the detector.
Lisun Instruments Limited was found by LISUN GROUP in 2003. LISUN quality system has been strictly certified by ISO9001:2015. As a CIE Membership, LISUN products are designed based on CIE, IEC and other international or national standards. All products passed CE certificate and authenticated by the third party lab.
Our main products are Goniophotometer, Integrating Sphere, Spectroradiometer, Surge Generator, ESD Simulator Guns, EMI Receiver, EMC Test Equipment, Electrical Safety Tester, Environmental Chamber, Temperature Chamber, Climate Chamber, Thermal Chamber, Salt Spray Test, Dust Test Chamber, Waterproof Test, RoHS Test (EDXRF), Glow Wire Test and Needle Flame Test.
Please feel free to contact us if you need any support.
Tech Dep: Service@Lisungroup.com, Cell/WhatsApp:+8615317907381
Sales Dep: Sales@Lisungroup.com, Cell/WhatsApp:+8618117273997
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *